Exiled opposition group says Iran hid nuclear weapons hub in desert

An exiled opposition group on Tuesday accused Tehran of operating a covert nuclear weapons program in the Semnan desert, an assertion that has not been independently verified.

An exiled opposition group on Tuesday accused Tehran of operating a covert nuclear weapons program in the Semnan desert, an assertion that has not been independently verified.
The National Council of Resistance of Iran (NCRI) said the desert zone, now designated a restricted military area, hosts the core of what it called the Kavir Plan—a successor to the earlier Amad project.
The United States accused Iran of seeking a nuclear weapon as part of the shadowy Amad Project scrapped before 2004, an effort Washington says was overseen by Iran’s Organization of Defensive Innovation and Research (SPND).
“Development, testing and nuclear weapons activities (are) hidden deep in the desert, under intense security measures,” the group’s spokesperson said at a press conference in Washington DC.
The announcement came as Tehran and Washington are negotiating over Iran's nuclear program to reach a deal to curb the program in return for the lifting of sanctions.
Washington has assessed that Iran is not building nuclear weapons and its Supreme Leader has not approved them but recent discourse in Tehran urging the acquisition a bomb is emboldening advocates for such a move.
US President Donald Trump on Tuesday said Iranian negotiators have become “much more aggressive” in recent weeks, confirming nonetheless that the sixth round of talks would take place this week.
Kavir Plan
NCRI’s leading faction, the Mojahedin-e-Khalq (MeK), said it had obtained new evidence from inside Iran.
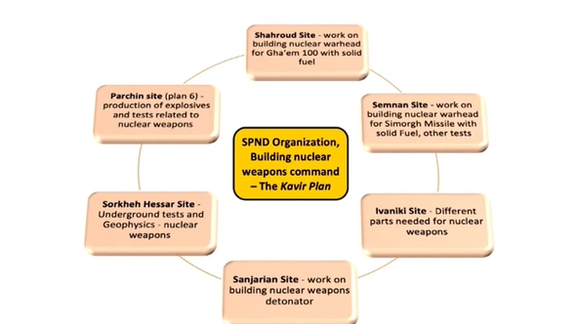
MeK spokesperson Alireza Jafarzadeh said the Kavir Plan involves at least six sites in Semnan province—Shahrud, Eyvanaki, Semnan, Sanjarian, Sorkheh Hesar and Parchin site in coordination with the SPND headquarters in Tehran—all directed by the Ministry of Defense and Revolutionary Guards.
“The Kavir Plan is not just a replacement for the Amad Plan, but it’s a more advanced, more sophisticated and more secure plan than the original one,” Jafarzadeh said.

According to NCRI, SPND serves as the coordinating body for Kavir activities. SPND was named in a 2011 IAEA report and sanctioned by the US in 2014 for proliferation efforts.
Jafarzadeh said over 400 nuclear specialists have been transferred from Iran’s Atomic Energy Organization to SPND operations under the Defense Ministry.
Among the sites, Shahrud was identified as a launch complex for Ghiam-100 solid-fuel missiles, allegedly disguised as a satellite facility. Sanjarian focused on explosive bridge wire (EBW) detonators—components critical for weaponizing a bomb, the opposition group added.
Iran has repeatedly denied pursuing nuclear weapons, dismissing MeK reports as fabrications.
"Building nuclear warheads"
The NCRI maintains that the Kavir Plan mirrors the Amad Plan’s goals—specifically, building five nuclear warheads designed for Shahab-3 missiles.
In 2002, the NCRI revealed for the first time a uranium enrichment facility at Natanz and a heavy water plant at Arak. In 2003, the group also disclosed the Lavizan-Shian Technological Research Center in northeastern Tehran as an undeclared nuclear site.
The Lavizan-Shian site was cited again in the UN nuclear watchdog’s May 2025 report for noncompliance and the presence of undeclared nuclear material.
Shayan Samiee, a national security expert, said the new report would heighten political pressure.
“I doubt that the intelligence and security apparatus of the US and Europe had no clue about this information. Surely they did,” he told Iran International TV.
“This report will put pressure on the House and Senate to push President Trump to either shut down negotiations with Iran or adopt a tougher stance.”
On Monday, Iran’s Supreme National Security Council said it had acquired sensitive documents linked to Israel’s nuclear program.
Tehran warned it will use those files to hit Israel’s clandestine nuclear facilities if the Jewish state attacks Iran.